On March 27, 2018, Basil Al-Otaibi, Senior Reservoir Engineer at Field Development Group, North Kuwait, delivered a lecture entitled "Lessons Learned from Water Injection in NK in the last two decades".
The lecture consisted of several parts:
• An overview of North Kuwait Fields
• History of water injection in North Kuwait
• Water injection management
• North Kuwait future requirements in terms of increased injection and associated projects
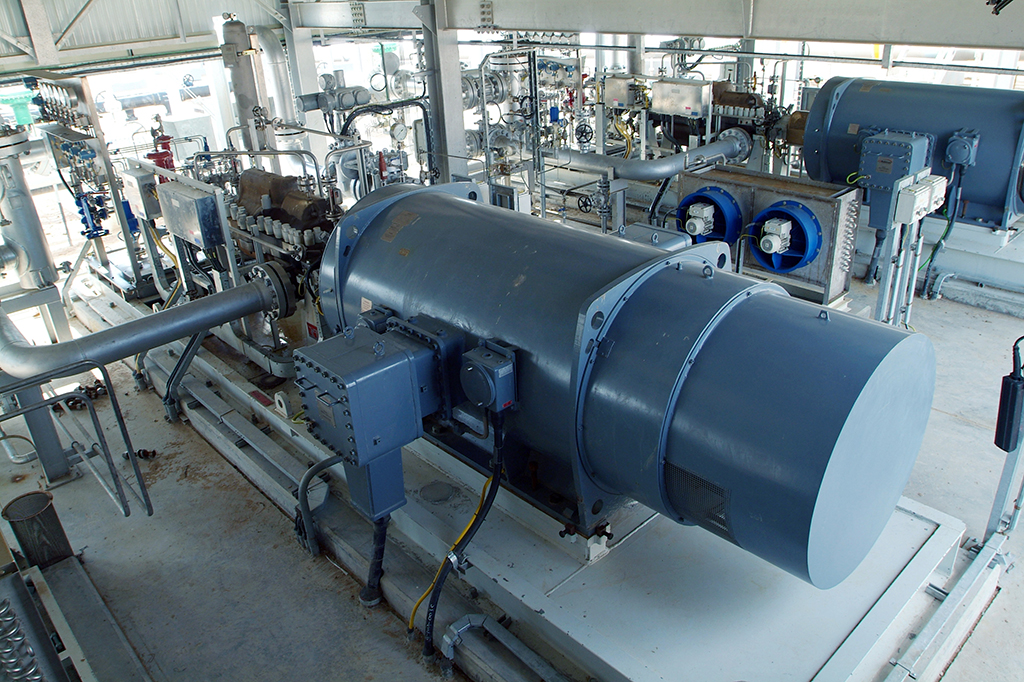

An overview of NK Fields
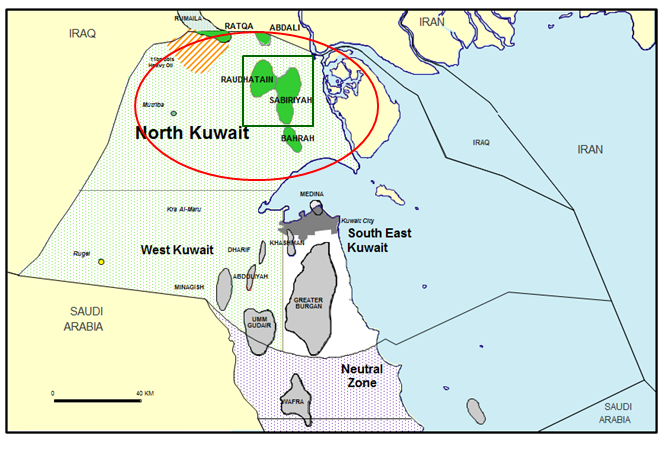
In the Directorate of North Kuwait, there are five fields, namely Bahrah, Sabriya, Rawdatain, Abdali and Ratqa. Out of seven main reservoirs, five are producing oil by water injection. Although the fields date back to the fifties of the last century, there is still a large amount of oil reserves that will be produced. There are more than 1000 production wells and 5 assembly centers in NK. The following map shows the fields north of Kuwait
History of Water Injection in NK
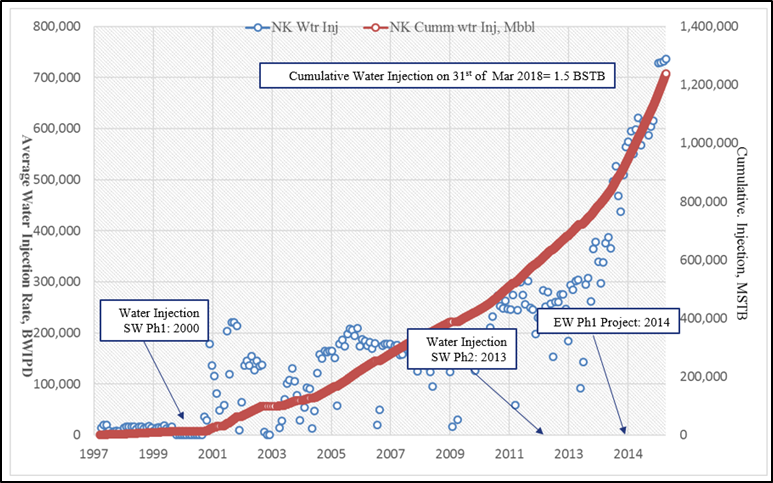
Injecting water into oil reservoirs is a means of raising pressure and thus helps to continue production in addition to pushing oil towards production wells. In North Kuwait water injection started in 1998, after experiments in the fields were successfully completed, which led to the expansion of the project to include Sabriya and Al-Rawdatin fields. Currently, over 900,000 barrels of water per day are injected into five major reservoirs. Two types of water are injected into reservoirs, namely seawater and water coming out of gathering centers. The following diagram shows the history of water injection projects in North Kuwait
Water Injection Management
One of the most important activities carried out by staff in the fields of NK is water management, which includes water production; injection and disposal.
These tasks are divided into two main parts:
1. Surface facilities including gathering centers and water injection plants
2. Water injection wells and oil reservoirs.
In order to create an integrated working environment between the two main sections, a workgroup was created, comprising staff from all teams interested in water projects in the fields. At the beginning of each year, a work plan is developed and all the tasks are implemented and followed up continuously. This method has improved the performance of water injection capacity, which increased the amount of injections by 25% in recent years, and thus had a positive impact on the performance and production of oil reservoirs.
Following are the most prominent activities of water management:
• Periodic review of water injection performance for the injected well and its impact on production wells surrounding it.
• Evaluating the effect of water injection on oil reservoirs in terms of increasing reservoir pressure and increasing production of reservoir oil.
• Comparison between the amount of water produced and the quantities required for future water injection.
• Study of the feasibility of future water injection projects.
• Determine water quality required for injection.
• Trying to find out quick solutions to increase the amount of water injection for existing surface facilities.
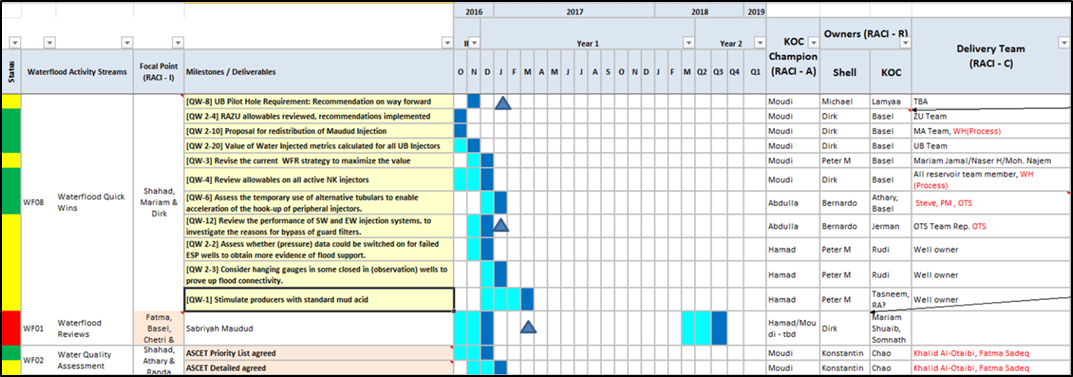
The following table shows an example of work plan at the beginning each year, the way in which interested people and teams are determined, and how to track their progress.
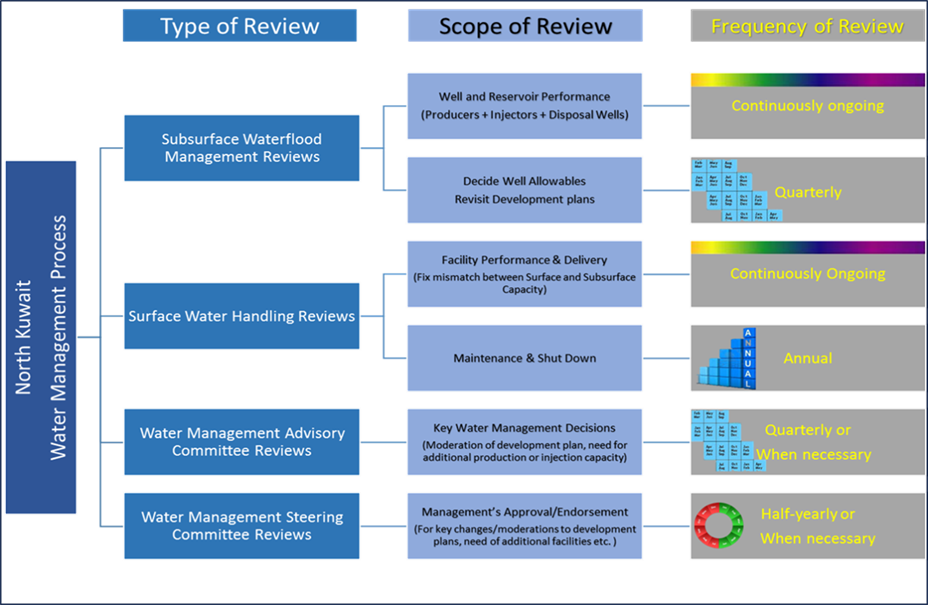
There is more than one water management committee in north Kuwait. The first is the technical committee consisting of engineers and geologists who constantly assess the performance of water management projects through periodic meetings of all wells and reservoirs. In addition, a similar committee is more interested in surface facilities. The Advisory Committee reviews the most important decisions on field development plan and improving future performance. The Higher Committee consists of the Upper Management of North Kuwait Fields Directorate, which approves or rejects the decisions of other committees
In future projects giant for the production and injection of water. The following table shows the grades of the various committees in northern Kuwait. This committee is interested in future production giant projects and water injection. The following table shows the status of various committees in North Kuwait.
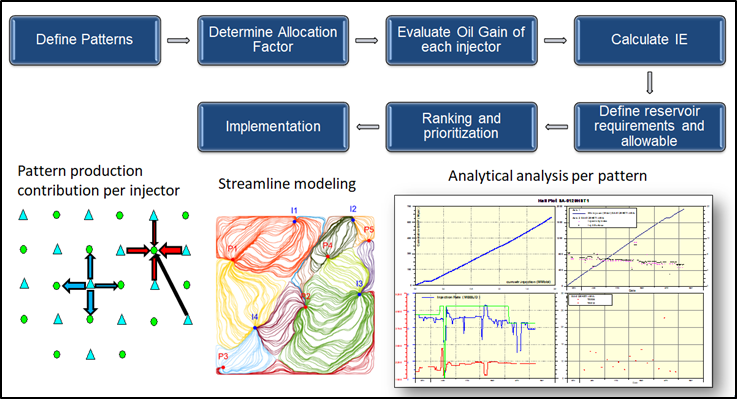
In order to ensure obtaining best results from water injection, the average daily requirement in each injection well is calculated quarterly. The injection rate for more than 100 wells is calculated as follows:
• Identifying the injection well and surrounding production wells
• Evaluating the amount of oil produced because of water injection
• Evaluating efficiency of each injected well
• Arranging a list of wells according to their efficiency
• Implementation
Several tools are used to accomplish this job such as:
• Reservoir simulation model
• History of wells performance according to database
• Previous information about different parts of reservoir
The following flowchart diagram illustrates details of this task
Future water projects in northern Kuwait
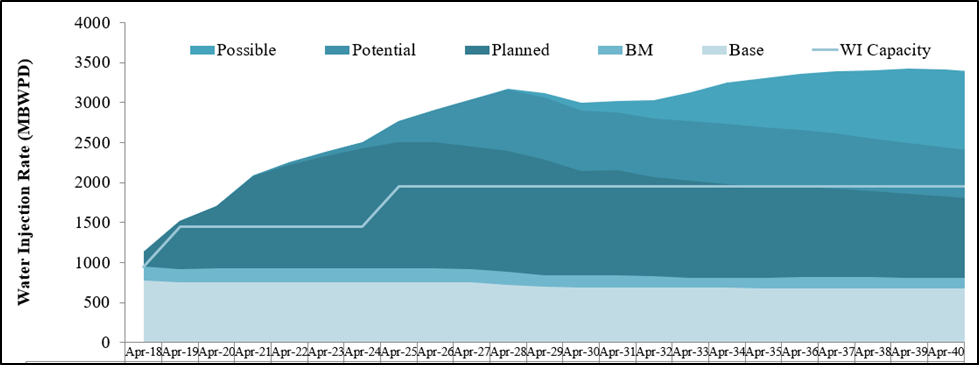
North Kuwait fields are the most important factor that will contribute to the achievement of the strategic objectives of KOC. In order to increase oil production in the next few years, there are many requirements to continue managing production associated water and inject it to enhance the capacity of oil reservoirs.
In 2019, water injection project from assembly centers will be operational with a capacity of 500,000 barrels per day. In 2025, a similar project with the same capacity would be available for North Kuwait. This water, which is separated from the oil produced, will be processed first before being injected into oil reservoirs to ensure that it conforms to the international standards of water quality. The following chart shows the future prospects for North Kuwait in terms of water injection requirements.
Lessons learned from the past two decades of water injection in NK:
• Water projects have proved to be of paramount importance to the continuity of oil production North Kuwait
• It is essential to establish a workgroup to manage water with to focus on assessing performance of water injection in oil reservoirs
• The use of technology will improve the efficiency of water management in both surface facilities, wells and reservoirs
• Future field requirements are increasing in order to contribute to the strategic objective of North Kuwait and KOC
• In short, the lack of water for injection means that it is impossible to continue production in North Kuwait

